Delayed cord clamping nct.
If you’re searching for delayed cord clamping nct images information related to the delayed cord clamping nct keyword, you have come to the right site. Our website always gives you hints for seeking the highest quality video and image content, please kindly search and find more informative video articles and graphics that fit your interests.
 Delayed Cord Clamping Banking Umbilical Cord Blood Smart Cells From smartcells.com
Delayed Cord Clamping Banking Umbilical Cord Blood Smart Cells From smartcells.com
Delayed cord clamping DCC from 30 to 60 seconds allows blood to continue to flow from the placenta through the umbilical cord to the infant thus resulting in a placental transfusion. DCC allows more blood to transfer from the placenta to the baby sometimes increasing the childs blood volume by up to a third. Maternal Blood Loss Cesarean Delivery Delayed Cord Clamping Neonatal Health. In response to this NCTs Chief Executive Belinda Phipps says.
Our specific aim is to determine if a 30 to 45 second delay in umbilical cord clamping improves neonatal outcome as assessed by a composite of intraventricular hemorrhage and late onset sepsis in preterm infants born between 24 and 32 weeks gestation.
There are some benefits for delayed cord clamping. NCT is thrilled to see yet another report that supports the practice of late cord clamping. Despite expert recommendations to delay clamping the cord for at least 2 minutes early cord clamping remains a common obstetrical practice. The iron in the blood increases the newborns iron storage which is vital for healthy brain development. In response to this NCTs Chief Executive Belinda Phipps says.
 Source: emmasdiary.co.uk
Source: emmasdiary.co.uk
In response to this NCTs Chief Executive Belinda Phipps says. So having read a few. DCC - Delayed Cord Clamping. There are some benefits for delayed cord clamping. Despite expert recommendations to delay clamping the cord for at least 2 minutes early cord clamping remains a common obstetrical practice.
States some important advantages of delayed cord clamping for healthy term infants such as a higher birthweight early peak haemoglobin concentration and increased iron reserves for up to six months after birth4 Delayed cord clamping does not seem to increase the risk of haemorrhage or other complications for low risk mothers.
There are some benefits for delayed cord clamping. Delayed umbilical cord clamping is usually performed 25 seconds to 5 minutes after giving birth. The best time to cut the umbilical cord of full term babies is unknown. Infants will be randomized into two groups based on the duration of delayed cord clamping.
 Source: smartcells.com
Source: smartcells.com
DCC - Delayed Cord Clamping. By Crystal RaypoleMay 24 20197 mins to read. The iron in the blood increases the newborns iron storage which is vital for healthy brain development. When the placenta is out your midwife will clamp and cut the cord.

A lot of studies have shown that delayed umbilical cord clamping is associated with greater haemoglobin concentration better iron storage between 3-6 months of life and lower incidence for transfusion and neonatal hypotension compared to immediate umbilical cord clumping. The best time to cut the umbilical cord of full term babies is unknown. Early iron sufficiency is essential for long term neurologic health. There are some benefits for delayed cord clamping.
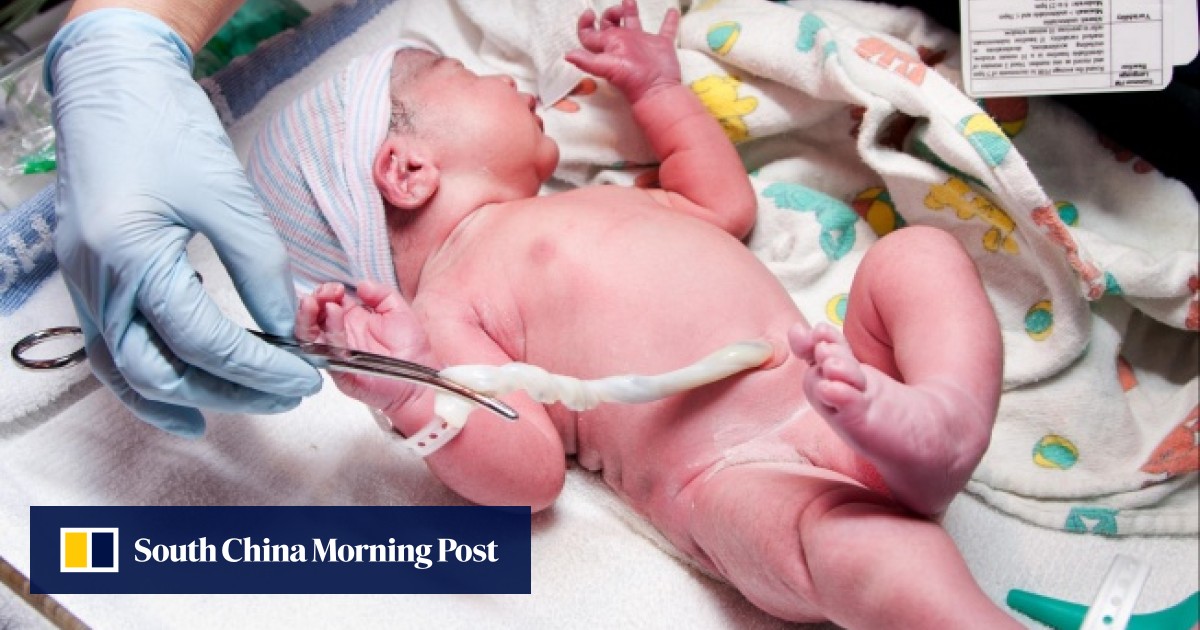 Source: scmp.com
Source: scmp.com
Early iron sufficiency is essential for long term neurologic health. Our specific aim is to determine if a 30 to 45 second delay in umbilical cord clamping improves neonatal outcome as assessed by a composite of intraventricular hemorrhage and late onset sepsis in preterm infants born between 24 and 32 weeks gestation. 45546 members 15338 posts. Delayed cord clamping was found to increase the incidence of jaundice in babies and the Cochrane authors recommend that where delayed cord clamping is practised there should be easy access to phototherapy4 Some clinicians argue that promoting physiological transition at birth by delaying cord clamping until respiration is established.
Delaying cord clamping for at least 30 seconds seems to benefit premature babies but its not yet known what the best length of delay above that is Rabe et al 2019. The best time to cut the umbilical cord of full term babies is unknown. States some important advantages of delayed cord clamping for healthy term infants such as a higher birthweight early peak haemoglobin concentration and increased iron reserves for up to six months after birth4 Delayed cord clamping does not seem to increase the risk of haemorrhage or other complications for low risk mothers. 45546 members 15338 posts.
This is not the first wave of evidence that highlights the benefits of delaying cord clamping for a few minutes to allow.
After delivery of a baby the umbilical cord is cut to separate the baby from the placenta and the mother. Different hemodynamic effects will be measured in each group at different time intervals. So having read a few. In response to this NCTs Chief Executive Belinda Phipps says. 45546 members 15338 posts.
 Source: emmasdiary.co.uk
Source: emmasdiary.co.uk
Different hemodynamic effects will be measured in each group at different time intervals. There are some benefits for delayed cord clamping. DCC - Delayed Cord Clamping. By Crystal RaypoleMay 24 20197 mins to read. 30 seconds vs 120 seconds.
Delayed cord clamping Intervention Type. This is not the first wave of evidence that highlights the benefits of delaying cord clamping for a few minutes to allow. Iron deficiency in infancy adversely affects cognitive motor socio-emotional and behavioral development. Delayed cord clamping was found to increase the incidence of jaundice in babies and the Cochrane authors recommend that where delayed cord clamping is practised there should be easy access to phototherapy4 Some clinicians argue that promoting physiological transition at birth by delaying cord clamping until respiration is established.
The best time to cut the umbilical cord of full term babies is unknown.
Different hemodynamic effects will be measured in each group at different time intervals. When the placenta is out your midwife will clamp and cut the cord. DCC allows more blood to transfer from the placenta to the baby sometimes increasing the childs blood volume by up to a third. Iron deficiency in infancy adversely affects cognitive motor socio-emotional and behavioral development.
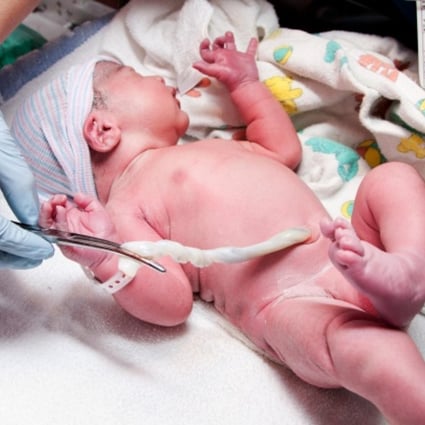 Source: scmp.com
Source: scmp.com
Delayed cord clamping DCC from 30 to 60 seconds allows blood to continue to flow from the placenta through the umbilical cord to the infant thus resulting in a placental transfusion. Maternal Blood Loss Cesarean Delivery Delayed Cord Clamping Neonatal Health. The iron in the blood increases the newborns iron storage which is vital for healthy brain development. Delaying cord clamping has been shown to increase early iron stores without contributing to adverse outcomes.
 Source: smartcells.com
Source: smartcells.com
This transfusion may improve circulating volume at birth leading to a smoother postnatal transition and overall improved outcome for preterm infants. The 40 mentioned by Melanie is a ball park figure might be slightly less if the cord is clamped right after a contraction which squeezes blood down the vein or much much more if baby is premature or oxygenation has been compromised by a tight cord or a difficult birth - in these circumstances it is even more important to leave the cord. Delayed umbilical cord clamping is usually performed 25 seconds to 5 minutes after giving birth. DCC - Delayed Cord Clamping.

Our specific aim is to determine if a 30 to 45 second delay in umbilical cord clamping improves neonatal outcome as assessed by a composite of intraventricular hemorrhage and late onset sepsis in preterm infants born between 24 and 32 weeks gestation. This transfusion may improve circulating volume at birth leading to a smoother postnatal transition and overall improved outcome for preterm infants. Umbilical cord can be clamped within 30s or at least 1 min after birth. This study aims to compare the effects of two different duration of delayed cord clamping.
This study aims to compare the effects of two different duration of delayed cord clamping.
The World Health Organization has noted that data on cesarean deliveries are more limited particularly with respect to long-term effects in infants. This transfusion may improve circulating volume at birth leading to a smoother postnatal transition and overall improved outcome for preterm infants. DCC - Delayed Cord Clamping. Delayed umbilical cord clamping is usually performed 25 seconds to 5 minutes after giving birth. The umbilical cord will be clamped as soon as feasible after birth usually within the initial 15 seconds after birth.
 Source: scmp.com
Source: scmp.com
The World Health Organization has noted that data on cesarean deliveries are more limited particularly with respect to long-term effects in infants. This is not the first wave of evidence that highlights the benefits of delaying cord clamping for a few minutes to allow. The best time to cut the umbilical cord of full term babies is unknown. Our specific aim is to determine if a 30 to 45 second delay in umbilical cord clamping improves neonatal outcome as assessed by a composite of intraventricular hemorrhage and late onset sepsis in preterm infants born between 24 and 32 weeks gestation. NCT is thrilled to see yet another report that supports the practice of late cord clamping.
NCT is thrilled to see yet another report that supports the practice of late cord clamping.
Umbilical cord can be clamped within 30s or at least 1 min after birth. DCC - Delayed Cord Clamping. Different hemodynamic effects will be measured in each group at different time intervals. By Denis CampbellJul 10 20134 mins to read.
 Source: smartcells.com
Source: smartcells.com
So having read a few. Delayed umbilical cord clamping is usually performed 25 seconds to 5 minutes after giving birth. DCC - Delayed Cord Clamping. Delayed cord clamping was found to increase the incidence of jaundice in babies and the Cochrane authors recommend that where delayed cord clamping is practised there should be easy access to phototherapy4 Some clinicians argue that promoting physiological transition at birth by delaying cord clamping until respiration is established.

DCC - Delayed Cord Clamping. This is not the first wave of evidence that highlights the benefits of delaying cord clamping for a few minutes to allow. DCC - Delayed Cord Clamping. The 40 mentioned by Melanie is a ball park figure might be slightly less if the cord is clamped right after a contraction which squeezes blood down the vein or much much more if baby is premature or oxygenation has been compromised by a tight cord or a difficult birth - in these circumstances it is even more important to leave the cord.
 Source: scmp.com
Source: scmp.com
Appt will there be birth plan speaking because I want to delay the clamping cord a few minutes. This is not the first wave of evidence that highlights the benefits of delaying cord clamping for a few minutes to allow. The World Health Organization has noted that data on cesarean deliveries are more limited particularly with respect to long-term effects in infants. The best time to cut the umbilical cord of full term babies is unknown.
The iron in the blood increases the newborns iron storage which is vital for healthy brain development.
States some important advantages of delayed cord clamping for healthy term infants such as a higher birthweight early peak haemoglobin concentration and increased iron reserves for up to six months after birth4 Delayed cord clamping does not seem to increase the risk of haemorrhage or other complications for low risk mothers. After delivery of a baby the umbilical cord is cut to separate the baby from the placenta and the mother. DCC - Delayed Cord Clamping. Delayed cord clamping was found to increase the incidence of jaundice in babies and the Cochrane authors recommend that where delayed cord clamping is practised there should be easy access to phototherapy4 Some clinicians argue that promoting physiological transition at birth by delaying cord clamping until respiration is established. Different hemodynamic effects will be measured in each group at different time intervals.
 Source: emmasdiary.co.uk
Source: emmasdiary.co.uk
Despite expert recommendations to delay clamping the cord for at least 2 minutes early cord clamping remains a common obstetrical practice. The umbilical cord will be clamped after 60 seconds after birth Arm Group Label. There are some benefits for delayed cord clamping. After delivery of a baby the umbilical cord is cut to separate the baby from the placenta and the mother. The umbilical cord will be clamped as soon as feasible after birth usually within the initial 15 seconds after birth.
Our specific aim is to determine if a 30 to 45 second delay in umbilical cord clamping improves neonatal outcome as assessed by a composite of intraventricular hemorrhage and late onset sepsis in preterm infants born between 24 and 32 weeks gestation.
The 40 mentioned by Melanie is a ball park figure might be slightly less if the cord is clamped right after a contraction which squeezes blood down the vein or much much more if baby is premature or oxygenation has been compromised by a tight cord or a difficult birth - in these circumstances it is even more important to leave the cord. Maternal Blood Loss Cesarean Delivery Delayed Cord Clamping Neonatal Health. Iron deficiency in infancy adversely affects cognitive motor socio-emotional and behavioral development. Despite expert recommendations to delay clamping the cord for at least 2 minutes early cord clamping remains a common obstetrical practice.
 Source: pregged.com
Source: pregged.com
NCT is thrilled to see yet another report that supports the practice of late cord clamping. The umbilical cord will be clamped after 60 seconds after birth Arm Group Label. Different hemodynamic effects will be measured in each group at different time intervals. Appt will there be birth plan speaking because I want to delay the clamping cord a few minutes. DCC - Delayed Cord Clamping.

Delayed umbilical cord clamping is usually performed 25 seconds to 5 minutes after giving birth. The World Health Organization has noted that data on cesarean deliveries are more limited particularly with respect to long-term effects in infants. Late clamping of the umbilical cord has been shown to have positive effects such as higher neonatal hemoglobin level higher iron stores in the newborn around three to six months and better neurological development. Delaying cord clamping for at least 30 seconds seems to benefit premature babies but its not yet known what the best length of delay above that is Rabe et al 2019. Delayed umbilical cord clamping is usually performed 25 seconds to 5 minutes after giving birth.
 Source: smartcells.com
Source: smartcells.com
Different hemodynamic effects will be measured in each group at different time intervals. Delaying cord clamping has been shown to increase early iron stores without contributing to adverse outcomes. By Denis CampbellJul 10 20134 mins to read. The World Health Organization has noted that data on cesarean deliveries are more limited particularly with respect to long-term effects in infants. 45546 members 15338 posts.
This site is an open community for users to submit their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site value, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title delayed cord clamping nct by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.





